A type of contract issued by a bank on behalf of a customer who has entered a contract to purchase goods from a supplier.
Read More
Irradiation is the process by which an object is exposed to radiation. The USDA states, “Food irradiation is a process in which approved foods are exposed to radiant energy, including gamma rays, electron beams, and x-rays. In 1963, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) found the irradiation of food to be safe.”
Food manufacturers may provide a statement confirming that their internal process does not include irradiation. While many companies don’t irradiate their food as a part of their normal food production process, imported products it may undergo a random and unavoidable x-ray checkpoint at the port of entry for safety purposes.
Read More
To bring a product into your home country from abroad.
Read More
See
Plastic Tote. IBC is a type of plastic, sometimes used in plastic caged totes.
A component or element of something. In food, it is any of the foods or substances that are combined to make a particular dish or retail product.
Read More
Hydrogenation is the chemical process by which liquid vegetable oil is transformed into solid fat. The process involves treating the oil with hydrogen; it is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element (usually the oil molecules). Hydrogenation also increases the shelf life and the flavor stability of oils and foods that contain them. An oil can be either fully hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated. Fully hydrogenated oils are solid, while partially hydrogenated oils are semi-solid (the consistency of margarine or butter). Partially hydrogenated oils were recently taken of the FDA’s
GRAS list because they contain trans fatty acids, or trans fats, which are harmful for our health. A fully hydrogenated oil doesn’t contain trans fats in the same way and are the new alternative to PHOs; when blended with liquid oils they make a semi-solid state.
Read More
An oil that has a high level of oleic acids (monounsaturated fats) in comparison to other versions of the same oil. Examples would be high oleic sunflower oil, which is made up of about about 80% oleic acid. This is in contrast to a linoleic sunflower oil, that has higher levels of linoleic acid (or polyunsaturated fat).
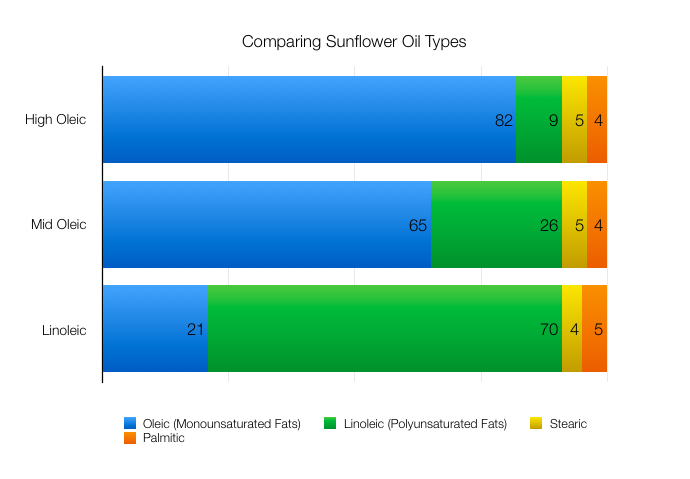
Read More
A heat treated pallet is one made from wood that has been heat treated prior to assembly. Heat treatment is a process whereby lumber is heated in a closed chamber until it reaches a core temperature of 56°C for at least 30 minutes in order to kill pathogens such as insects, fungi, or micro-organisms. It is ideal for export purposes, as it helps reduce the spread of wood-born diseases and organisms into new countries.
Read More
A halal statement is a food safety document provided by food manufacturers, showing that their products are processed in such a way that fits the Muslim prescription for how meat should be prepared. Halal means “permissible” or “allowed” in Arabic, and involves a few different stipulations and/or requirements for meat preparation.
Read More
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, or HACCP, is a systematic preventive approach to food safety from biological, chemical, and physical hazards in production processes that can cause the finished product to be unsafe. A HACCP plan designs measures to reduce these risks to a safe level. It is usually presented in the form of a detailed food safety related document, and is provided by food manufacturers and processors to customers.
Read More
