This article was originally published by Centra Foods in 2014, and has been re-published with updated information here.
Sometimes, it's hard to know exactly what kind of oil is going to work best. If you're in the R&D stages of a new product, you'll be faced with decisions about choosing the right bulk ingredients. Sometimes, as you begin to narrow down your search, you may be presented with more and more challenging questions.
Let’s pretend you’ve finally made the decision to go with Sunflower Oil. Next, you’ll be immediately presented with a new question:
What kind of Sunflower Oil would you like?
Certain oils, especially seed oils, come in a few varieties. For sunflower oil, there’s three main types: high oleic, mid oleic and linoleic.
The Basic Differences Between High Oleic, Mid Oleic And Linoleic Sunflower Oil
The difference between each type of sunflower oil is a result of the balance between the polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats in the oil, which are linoleic acid and oleic acid, respectively. Each differ in oleic and linoleic chemical levels in the oil, as a result of the seeds that are grown.
High oleic oils are considered the most healthy, and have the most monosaturated fat (oleic) that makes up the oil. Linoleic is comprised of more polyunsaturated fats (considered a less healthy fat) and mid-oleic falls somewhere in between.
Keep in mind, all types of Sunflower Oil are non-GMO. There are currently no GM varieties available, making this a low-risk ingredient if you are getting your product Non-GMO Project Verified.
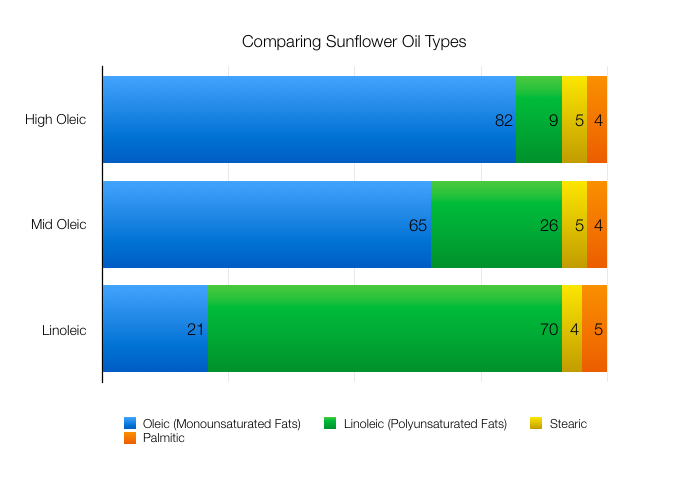
Before we review the details, here's a chart to reference the typical fatty acid profiles of each type.
Linoleic Sunflower Oil
Traditional sunflower oils have fallen into two categories, one high in oleic acid and the other high in linoleic acid. We’re going to first approach the oil that’s high in linoleic acid.
Linoleic acid is one of the essential fatty acids in the human diet, and linoleic varieties of sunflower oil contain nearly 70 percent polyunsaturated fat (linoleic acid). Another 20 percent is in monounsaturated fat (oleic acid), and the remaining 10 to 11 percent is saturated fat.
This linoleic sunflower oil is considered one of the least healthy types of sunflower oil, in comparison to high oleic oils that contain more healthy fats.
It is now produced in very small volumes in North America, because of it’s limitations in fried foods. It is, however, the traditional type of sunflower oil that’s been produced for many years.
High-Oleic Sunflower Oil
High-oleic sunflower oil is radically different than linoleic in its makeup. It consists primarily of monounsaturated fat (oleic acid), at around 80+ percent of the total. Saturated fats and polyunsaturated fats (linoleic acid) make up the balance, in equal proportions.
Bulk high-oleic sunflower oil is important in the manufacture of food products, because it remains stable without hydrogenation and will not go rancid in long-term storage. This makes switching from bulk linoleic to bulk high-oleic sunflower oil an easy way for manufacturers to reduce trans fats and increase their shelf life limitations.
This high oleic sunflower oil is preferred by food manufacturers because of it’s added stability and neutral taste profile. It’s an ideal oil for frying, baking and other high heat applications.
High oleic sunflower oil can be produced through expeller pressing methods or solvent extraction, so make sure that you confirm which type you are looking for with your supplier.
Mid-Oleic Sunflower Oil
Mid-oleic sunflower oil is the most common type of sunflower oil available in the US and Canada. It is considered the ‘standard’ sunflower oil in North America. It’s available in large volumes and is reasonably price competitive with other oils like canola and soybean oil.
Mid-oleic sunflower oil takes a middle position between the two traditional oils, with oleic acid accounting for roughly two-thirds of the fat content (65%), polyunsaturated linoleic acid at roughly 25 percent, and about 10 percent saturated fat. Mid-oleic oil retains high enough levels of linoleic acid to remain an excellent dietary source, but the relatively high levels of oleic acid make it less prone to rancidity and breaking down, eliminating any need for hydrogenation and the resulting trans fat.
This is typically the sunflower oil that you will buy at a retail store. It is most often a solvent expelled oil.
Learn More About Sunflower Oil
Want to learn more about sunflower oil? Choose one of the topics below to learn more:
Topics: Sunflower/Safflower Oil












